
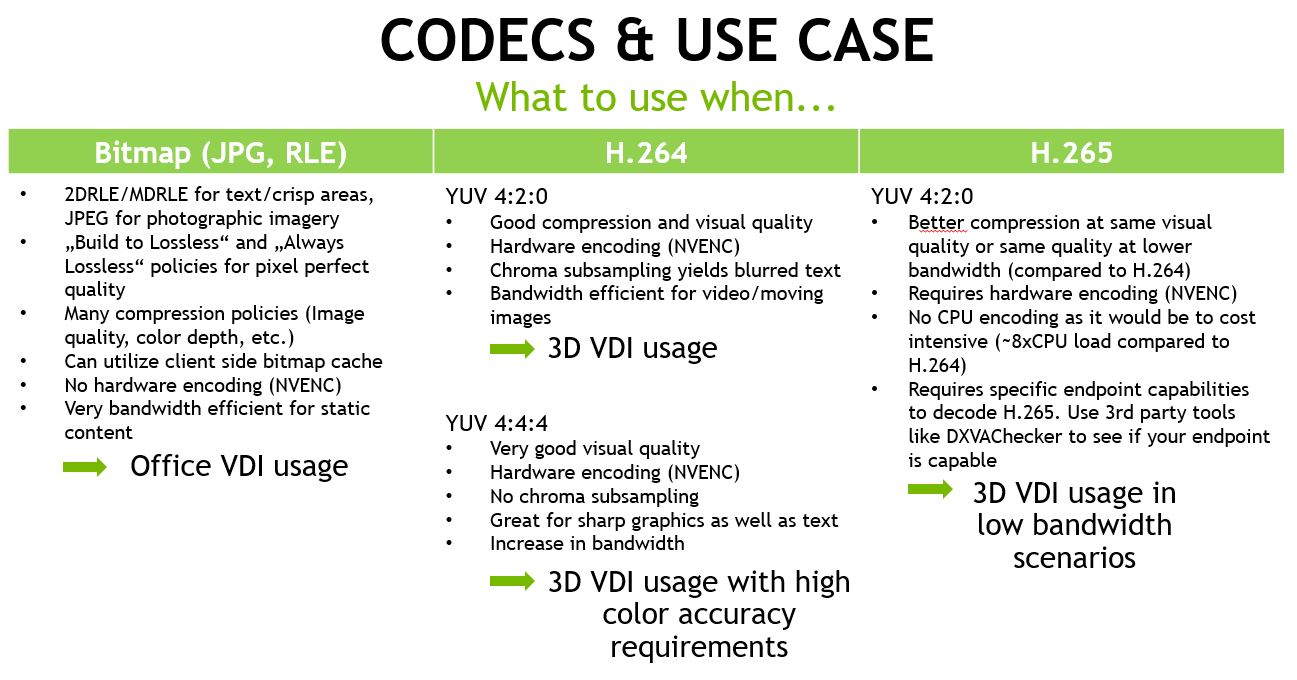
If H.265 promises more efficient compression, then it would only make sense to adopt a codec that offers better quality, higher accuracy, and uses less bandwidth, right? This allows commercial venues to broadcast live sports games, display video messaging, and control digital signage without losing picture quality. What does this mean for AV Integrators?ĪV over IP is the new industry paradigm, and H.264 delivers high-resolution video without hogging the bandwidth like its predecessors. Additionally, H.264, comes with nine prediction modes, while H.265 offers 34 prediction modes – again, equating to greater accuracy and quality when using large 4k video blocks. Mathematically generating values dramatically reduces the size of each frame making compression more efficient.

These CUs are then divided further into different prediction units allowing for the mathematical generation of pixel values, rather than storing them.

The coding tree units can also decrease in size to 8×8 pixel coding units (CU), which work to improve intraframe compression. CTUs can actually range from 16 x16 pixels to 64 x 64 pixels, and these larger blocks are necessary for efficient 4k stream encoding. While AVC uses a 16 x16 pixel macroblock structure, best suited for 1080p, HEVC uses coding tree units (CTUs). H.265, the seemingly cooler, younger sibling of revolutionary H.264, promises even better video quality using lower bitrates. HEVC stands for high-efficiency video codec and is a more complex method of video compression. In 2013, Samsung Electronics, GE, NTT, and JVC Kentwood developed a new video coding format called H.265 (HEVC). H.264 is also “over the network-friendly.” That is, AVC works by encoding audio-video signals and distributing them over the network, many times to multiple devices simultaneously without hogging the bandwidth like its predecessors. What does this mean to you? It means that you get to watch those funny cat videos on YouTube in the highest quality and without the screen freezing. The H.264 video codec processes frames into the motion-compensation video compression standard using macroblocks and is frequently formatted to the. H.264, also known as Advanced Video Coding (AVC), is the current industry-standard for high definition video compression that allows for the recording, compression, and distribution of digital video content. This brings us to 2003: H.264 developed by Panasonic, LG Electronics, and Godo Kaisha IP Bridge. The computer then converts this digital file back into the original format for our viewing pleasure (decompression).ġ980s: H.261 developed by Hitachi, Toshiba, and othersġ991: MPEG-1 developed by Motion Picture Experts Groupġ994: MPEG-2 / H.262 developed by Sony, Thomson, Mitsubishiġ999: MPEG-4 / H.263 developed by Mitsubishi, Hitachi, and Panasonic Video codecs convert light and sound from a camera into a digital file for a computer to read (compression).
The 1980s saw the rise of better video codecs and the fall of VHS, along with its Blockbuster slogan, “Be Kind, Rewind.” Video Codec stands for video compression and decompression.

Is it H.264? H.265? Something else entirely? We’re here to help! Video Coding – A Brief History Behind the scenes, their video encoder failed somewhere along the way and the bar is paying a hefty price for angry customers.Īs an AV integrator, it’s imperative to choose a reliable encoder and video compression standard that works for the commercial application. This may seem like a worst-case scenario for you, but it’s an even bigger nightmare for the bar. Just before another player makes the game-winning catch…the display pixelates – or even worse – the picture cuts out. Imagine this: You’re sitting at your local sports bar, enjoying a drink, and watching your favorite quarterback throw a pass into the end zone. H.265 Encoding for Commercial Applications


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
